
Essential anatomy 3 controls skin#
The surface tissue of skin is a barrier that protects internal structures and fluids from potentially harmful microorganisms and other toxins. The body’s largest organ system is the integumentary system, which includes the skin and its associated structures, such as hair and nails. In the chest and abdomen, a variety of internal membranes keep major organs such as the lungs, heart, and kidneys separate from others. Blood vessels keep blood inside a closed circulatory system, and nerves and muscles are wrapped in connective tissue sheaths that separate them from surrounding structures.
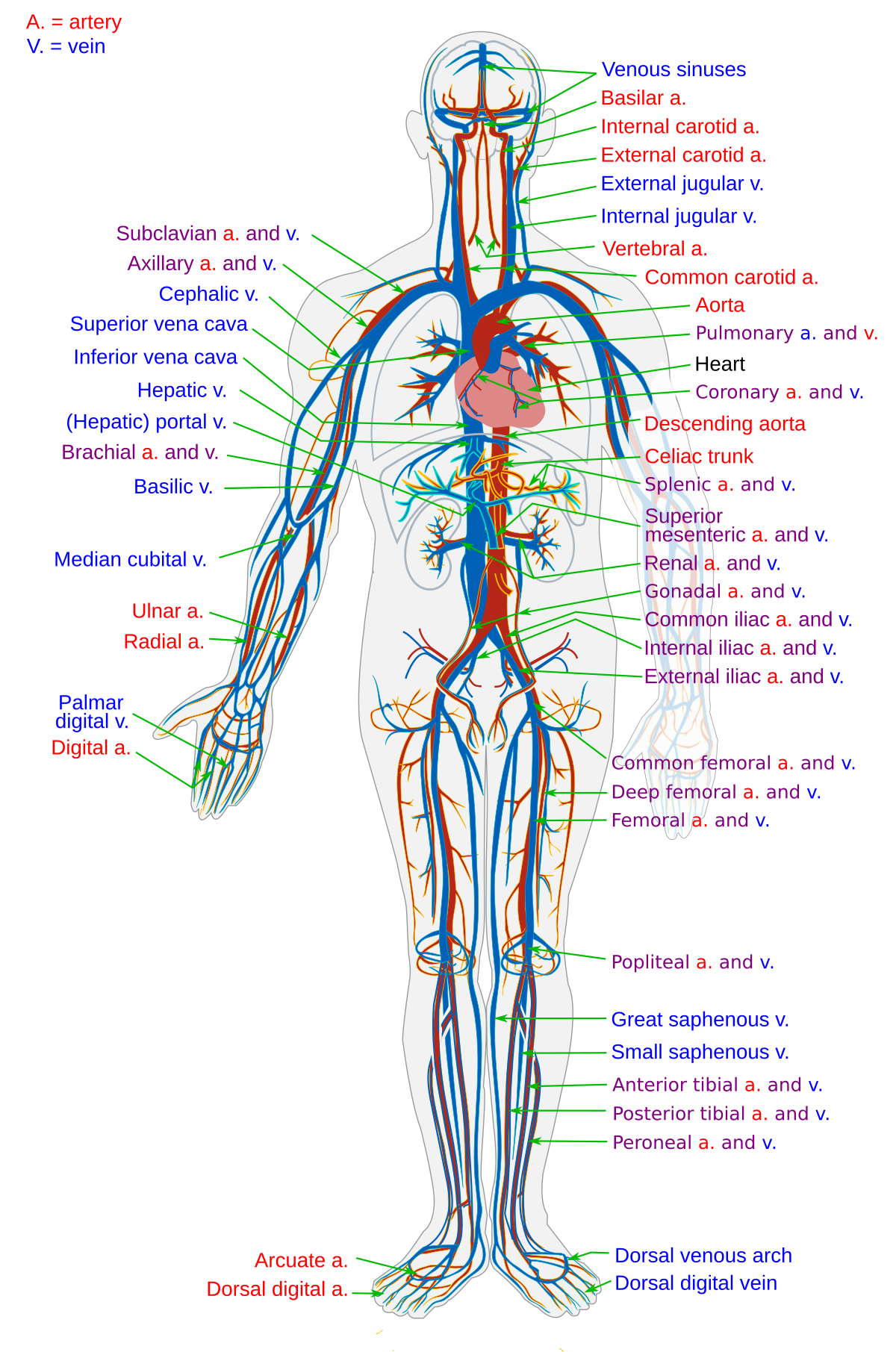
The intestinal tract, for example, is home to more bacterial cells than the total of all human cells in the body, yet these bacteria are outside the body and cannot be allowed to circulate freely inside the body.Ĭells, for example, have a cell membrane (also referred to as the plasma membrane) that keeps the intracellular environment-the fluids and organelles-separate from the extracellular environment.
They also separate internal body fluids from the countless microorganisms that grow on body surfaces, including the lining of certain passageways that connect to the outer surface of the body. These compartments keep body cells separated from external environmental threats and keep the cells moist and nourished. OrganizationĪ human body consists of trillions of cells organized in a way that maintains distinct internal compartments. These many functions can be summarized in terms of a few that we might consider definitive of human life: organization, metabolism, responsiveness, movement, development, and reproduction. The different organ systems each have different functions and therefore unique roles to perform in physiology. Compare and contrast growth, differentiation, and reproduction.Provide at least two examples of human responsiveness and human movement.Distinguish between metabolism, anabolism, and catabolism.Explain the importance of organization to the function of the human organism.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
